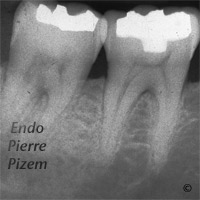
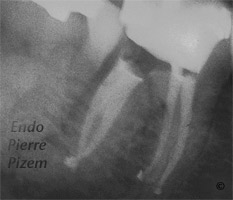
Vertucci’s Type III canal configuration
One canal leaves the pulp chamber and divide into two in the root; the two then merge to exit as one canal (1-2-1).
According to Vertucci’s study in 1984, the percentage of human permanent teeth with this canal configuration are 5 % for the maxillary second premolar and 0% for mandibular first and second molars. This post operative X Ray shows (once the huge denticle has been removed in coronal third) that the Vertucci’s Type III canal configuration is actually existing in a mandibular first molar.
As stated by Vertucci’s and al.
The pulp canal system is complex, and canals may branch, divide, and rejoin.

Leave a Reply