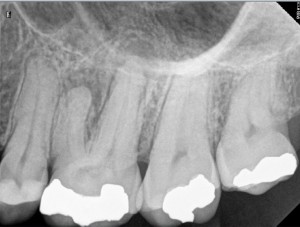
The patient was experiencing a daily constant nagging pain for the last 2 months. Pain increased along with some gum swelling the during last two days. Tooth is calcified thus its root canals are narrow and the pulp chamber is filled with pulp stones. Locating narrow root canals entries can be done in an much easier way under high magnification. In such instances a dental operative microscope is mandatory.
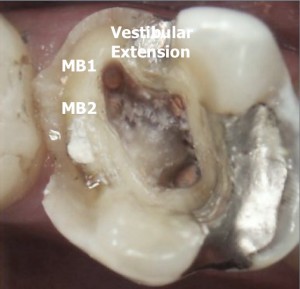
Palatal as well as DB could easily be located after pulp stones removal with Spartan BUC One ultrasonic tip and a P5. MB1 as been located by extending the access cavity toward buccal. Under full strength microscope magnification, MB2 canal entry has been located under a 2 millimeters thick layer of sclerotic dentin.
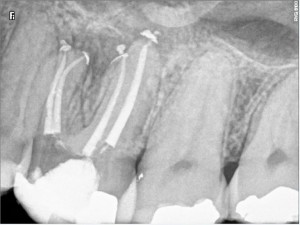
Since a purulent exsudat was present, root canal apical preparations are large. Ca(OH)2 dressing was left in place for ten days and root canals have then been filled in a subsequent appointment.
Instrumentation has been performed with Mani stainless K files and ProTaper Universal (Dentsply). Chelator: RC Prep. PUI Irrigation: NaOCl 5%. Sealer used: Pulp Canal Sealer. Obturation technique WVC. X Ray Sensors used: CareStream Kodak 6100. Magnification OPMI PROergo (Carl Zeiss)

Leave a Reply